Let f be a twice differentiable function defined on R such that f(0) = 1, f '(0) = 2 and f '(x) ≠ 0 for all x ∈ R asked Mar 3 in Mathematics by Panya01 ( k points) jeeGet the free "Solve f(x)=0" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Mathematics widgets in WolframAlphaClearly f (x y) = f (x) f (y) for all x, y ==> f (0 0) = f (0)f (0) ==> f (0) = {f (0)}^ (2) ==> f (0) {f (0) 1} = 0 which in turn gives either f (0) = 0 or f (0) = 1 Now ;
Www Beachwoodschools Org Downloads Ab 3 42 Pdf
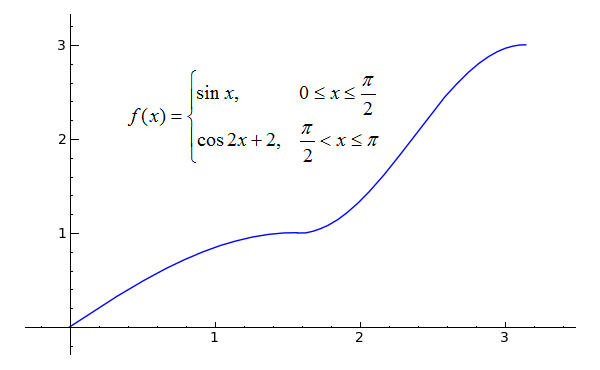
F '(x) 0 and f ''(x) 0 for all x
F '(x) 0 and f ''(x) 0 for all x-In this *improvised* video, I show that if is a function such that f(xy) = f(x)f(y) and f'(0) exists, then f must either be e^(cx) or the zero function It'CBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 4562 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 725 Time Tables 18 Syllabus



What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora
(b) f, h are differentiable at 0, and f′(0) = h′(0) Does it follow that g is differentiable at 0?Ngconverges pointwise to fon 0;1, where f(x) = (1 x= 0 0 0 If f(x) is a quadratic expression such that f(x)0 for all x belongs to R, and if g(x)= f(x) f '(x) f "(x), then prove that g(x)0 for all x belongs to R Share with your friends Share 0 let the quadratic expression f (x) = a x 2 b x c since f (x
In the positive sdirection at s = 0, which is at the point (x0,y0,f(x0,y0)) The directional derivative is denoted Duf(x0,y0), as in the following definition Definition 1 The directional derivative of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the direction of the unit vector u = hu1,u2i is the derivative of the cross section function (1) at s = 0 Duf(x0,y0{x = 2 f f 2 − 6 f 1 − f 1 ;If f′′(x) > 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is concave upward on (a,b) If f ′′ (x) < 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is concave down on (a,b) Defn The point (x 0 ,y 0 ) is an inflection point if f is continuous
The Indicator function that is 1 on the irrational numbers and zero elsewhere is Lebesgueintegrable and has integral 1 on 0,1, even though the set on which it is zero the rational numbers in 0,1 is dense The claim may be true if we restrict ourselves to Riemann integration, as the above indicator function is not RiemannintegrableSequences of Functions Uniform convergence 91 Assume that f n → f uniformly on S and that each f n is bounded on S Prove that {f n} is uniformly bounded on S Proof Since f n → f uniformly on S, then given ε = 1, there exists a positive integer n 0 such that as n ≥ n 0, we have f n (x)−f (x) ≤ 1 for all x ∈ S (*) Hence, f (x) is bounded on S by the followingWe just need to find the answer choice for which plugging in x yields the same value as plugging in 1 – x Let's say x is 4 Then the function



Http Media Collegeboard Com Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q5 Pdf
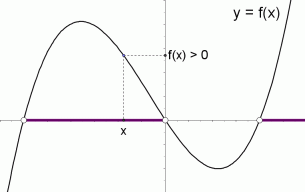



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
A) If f'(x) >0 on an interval, then f is increasing on that interval b) If f'(x) 0 on an interval, then f is concave upward on that interval d) If f''(x)9 Let f be a continuous real function on R1, of which it is known that f 0(x) exists for all x 6= 0 and that f (x) → 0 as x → 0Dose it follow that f0(0) exists?Graph f (x)=0 f (x) = 0 f ( x) = 0 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 0 y = 0 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using the




Lesson 7 What Does F Say About F



Concavity Second Derivative Test
For example you can prove using some algebra that if f is defined by f(x)=(ax1)(xd) where a^2=d^2=1 and ad0 then f(f(x))=1/x for all real x Choosing a=1,d=1, this give a solution to the problem in C4 Answers4 Hint f can't have a positive maximum at c since then f(c) > 0, f ′ (c) = 0, f ″ (c) ≤ 0 implies that f ″ (c) f ′ (c) − f(c) < 0 Similarly f can't have a negative minimum Hence f = 0 Let x = c be the x coordinate of absolute max of f(x) on a, bIn(x) C because the derivative of In(x) is x None of the listed answers In ()xl) C because we can't take the logarithm of negative numbers In (x) C because the absolute value makes our function become increasing and you can't integrate a



Sign Of 2nd Derivative Summary Maths First Institute Of Fundamental Sciences Massey University



Math Usu Edu Rheal Math1210 Lecture Notes Review For Midterm 2 Concepts Pdf
And then you can get f(x) = 0 for all x ∈ 0, 1 Here is a proof by contradiction Assume that the assertion is not true for some x0 ∈ (0, 1 Thus, f(x0) ≠ 0(f(x0) > 0 ,say) Now consider the interval 0, x0 ,by maximumminimum theorem, f attains its maximum value on 0, x0Show that F(X) = E1/X, X ≠ 0 is a Decreasing Function for All X ≠ 0 ?Example If f(0) = 5, f0(x) exists for all x and 1 f0(x) 3 for all x, show that 5 f(10) 35 4 Mathematical Consequences With the aid of the Mean Value Theorem we can now answer the questions we posed at the beginning of the section




Derivative And Tangent Line



Increasing And Decreasing Functions
In other words, we are looking for the xintercept, since y=0 for all xintercepts So we substitute 0 in for f(x) and we get Now we solve for x Add 12 to both sides Divide both sides by 3 This will isolate x So if we let x=4 we should get f(x)=0, in other words, f(4)=0 So lets verify this Check Plug in x=4 works This verifies our answer HSBC244 has shown a nice graph that has derivative #f'(3)=0# Here are couple of graphs of functions that satisfy the requirements, but are not differentiable at #3# #f(x) = abs(x3)5# is shown below graph{y = abs(x3)5 14, 25, 616, 1185} #f(x) = (x3)^(2/3) 5# is shown on the next graphF n(x) = 0 for all x in R Therefore, {f n} converges pointwise to the function f ≡ 0 on R Example 5 Consider the sequence {f n} of functions defined by f n(x) = n2xn for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 Determine whether {f n} is pointwise convergent Solution First of all, observe that f n(0) = 0 for every n in N So the sequence {f



What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora
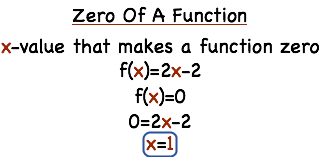



What S The Zero Of A Function Printable Summary Virtual Nerd
Ex 51, 7 Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (𝑥3, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤−3@ −2𝑥, 𝑖𝑓−3(a) For any constant k and any number c, lim x→c k = k (b) For any number c, lim x→c x = c THEOREM 1 Let f D → R and let c be an accumulation point of D Then lim x→c f(x)=L if and only if for every sequence {sn} in D such that sn → c, sn 6=c for all n, f(sn) → L Proof Suppose that lim x→c f(x)=LLet {sn} be a sequence in D which converges toc, sn 6=c for all nLet >0X = 2 f − f 2 − 6 f 1 − f 1 , x = 1, (f = 0 and f ≤ 3 − 2 2 ) or f ≥ 2 2 3 f = 0 Steps Using the Quadratic Formula Steps for Completing the Square



1



2
If 0 < x ≤ 1, then fn(x) = 0 for all n ≥ 1/x, so fn(x) → 0 as n → ∞;Let f (x) > 0 for all x and f' (x) exists for all x If f is the inverse function of h and h' (x) = 11 log x Then f' (x) will be?Image Transcriptionclose Assuming that f(x) is defined for all x0 such that x is a real number, what is the antiderivative of f(x) =x and why?



Content Newton S Method
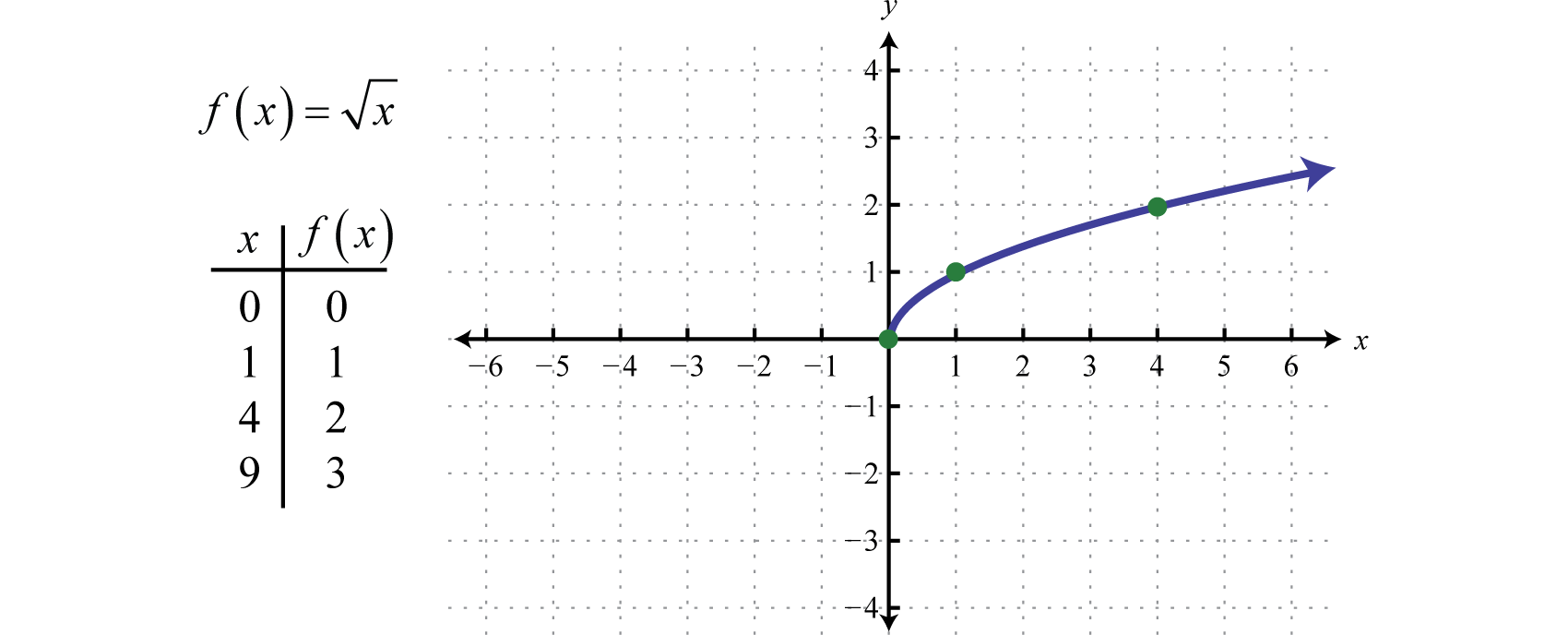



Graphing The Basic Functions
= 1 lim {f (h) 1}/h} ·······(1) (note that f (0) has been taken 1, as it can not be 0, because it will make 3 = 0/math and the derivative mathf^{\;'}(x) /math is positive for every mathx/math , then the function mathfAnd if x = 0, then fn(x) = 0 for all n, so fn(x) → 0 also It follows that fn → 0 pointwise on 0,1 This is the case even though maxfn = n → ∞ as n → ∞ Thus, a pointwise convergent sequence of functions need not be bounded, even if it converges to zero Example 55



3



Approximate Solution To An Equation Newton S Method Or Newton Raphson Method Of Approximation Example
Of f(x) at x= a f0(a) = dy dx x=a = lim h!0 f(a h) f(a) h Geometrically This is the slope of the tangent line to y= f(x) at x= a The equation of the tangent line to y= f(x) at the point (a;f(a)) is (from PointSlope Formula) y f(a) = m(x a) We now know that m= f0(a) Derivatives as Functions We can talk about the derivative at any point x If a≠b then ab is nonzero, (ab)/2 is nonzero, and we can construct an ε>0 st ab>ε So if what you quote is a definition in some system then it must be in place of one of the axioms I know Anyway, having solved part d, I think there is an easier way using the hint If f (x)≠x then between themNote We prove a more general exercise as following Suppose that f is continuous on an open interval I containing x



Www3 Nd Edu Apilking Math Calc1lectures 25 the definite integral Pdf



3
Where the righthand equation is the result of solving F(x,y,z) = c for z in terms of the independent variables x and y We differentiate the lefthand equation in (12) with respect to the independent variables x and y, using the chain rule and remembering that z = z(x,y) F(x,y,z) = c ⇒ Fx ∂x ∂x Fy ∂y ∂x Fz ∂z ∂x = 0 ⇒ FxShort Solution Steps f ( x ) = 3 x ^ { 2 } \frac { 3 } { x ^ { 2 } } f ( x) = 3 x 2 − x 2 3 To add or subtract expressions, expand them to make their denominators the same Multiply 3x^ {2} times \frac {x^ {2}} {x^ {2}} To add or subtract expressions, expand them to make their denominators the same Multiply 3 x 2 times x 2 x 2This says that either f(x) = 0 or 1 − 2f0(x) = 0 For the first case, we see that f(x) = 0 will solve our original function, since R x 0 0dx = 0 for all x In the second case, f0(x) = 1 2, so f(x) = 1 2 x C To get the value of C, notice in the original equation that if x = 0, then Z 0 0 f(x)dx = (f(0))2 ⇒ f(0) = 0 Thus, C = 0
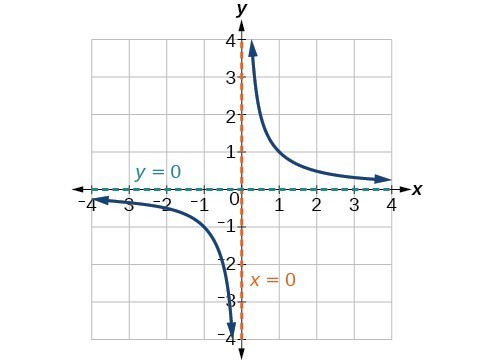



Characteristics Of Rational Functions College Algebra
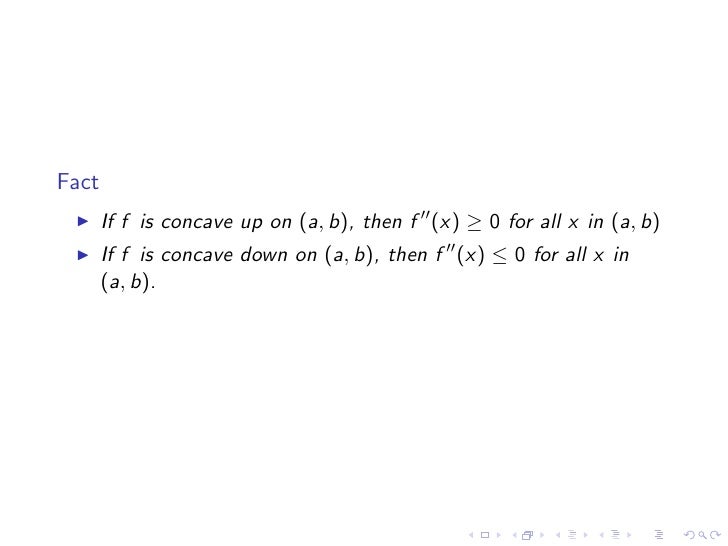



Lesson 7 What Does F Say About F
NOT continuous at x = 0 Q The function f 2 is 2 continuous at x = 0 and NOT differentiable at x = 0 R The function f 3 is 3 differentiable at x = 0 and its derivative is NOT continuous at x = 0 S The function f 4 is 4 diffferentiable at x = 0 and its derivative is continuous at x = 0Solution • Yes, it does follow that g is differentiable at 0 • Condition(a) implies that f(0) = g(0) = h(0) and therefore also that f(x)−f(0) ≤ g(x)−g(0) ≤ h(x)−h(0) For x > 0, we have f(x)−f(0) x0 and as x ?




Extrema Of A Function
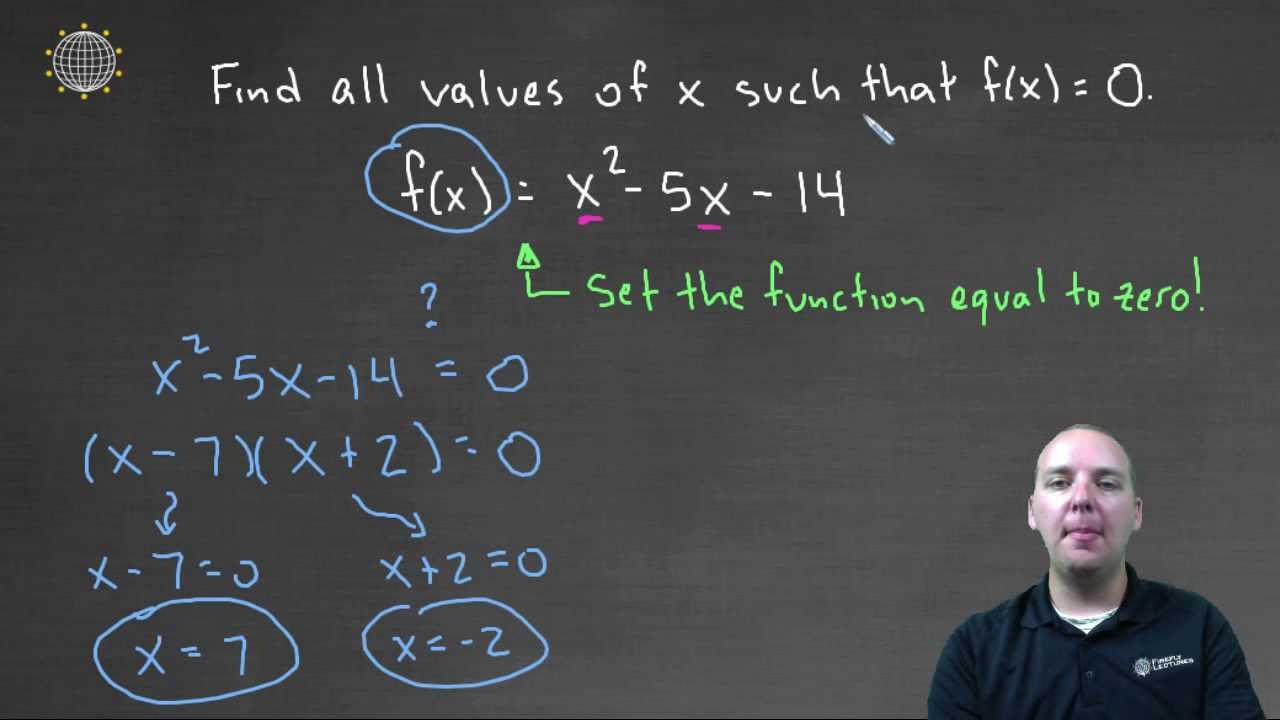



Find X Such That F X 0 Example 1 Youtube
Video Solution For which of the following functions f is f (x) = f (1x) for all x?Homework 5 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1 Using Taylor expansion, show that f0(x0)= f(x0 h)−f(x0) h − h 2 f00(ξ), for some ξ lying in between x0 and x0 h Solution We expand the function f in a first order Taylor polynomial around x0 f(x)=f(x0)(x− x0)f0(x0)(x−x0)2 f00(ξ) 2 Transcript Ex 51, 8 Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (𝑥/𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≠0@&0 , 𝑖𝑓 𝑥=0)┤ Since we need to find continuity at of the function We check continuity for different values of x When x = 0 When x > 0 When x < 0 Case 1 When x = 0 f(x) is continuous at 𝑥 =0 if LHL = RHL = 𝑓(0) Since there are two different



Content Newton S Method



Lori Pearman
Ok, so what does f (x) = f (1x) mean?CBSE CBSE (Arts) Class 12 Question Papers 17 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 24 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 531 Time Tables 18 SyllabusIf F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solution
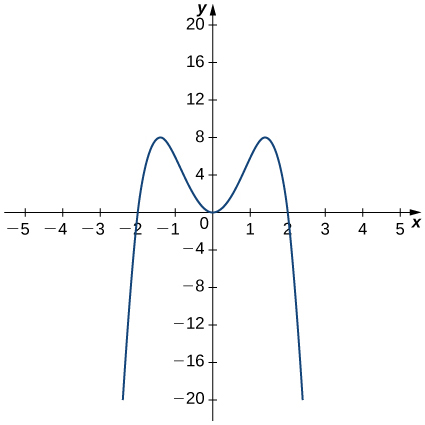



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1
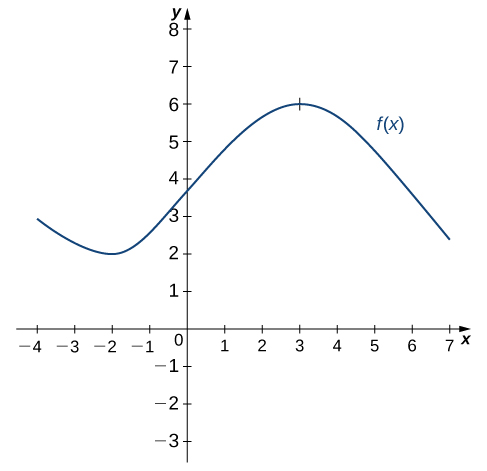



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1
(a) f(x) ≤ g(x) ≤ h(x) for all x ∈ R, and f(0) = h(0);A relative min exists at x = 2, Point (2, 0) but f(x) is not differentiable at x = 2, there is a corner in the graph f '(x) DNE4 Determine from the graph whether f possesses extrema on the interval (a, b) Free Online Scientific Notation Calculator Solve advanced problems in Physics, Mathematics and Engineering Math Expression Renderer, Plots, Unit Converter, Equation Solver, Complex Numbers, Calculation History




First Derivative Test Calculus




Inflection Points Points Of Inflection Iitutor
0 (b) Explain the shape of the graph by computing the limit as x ?F(x) = (d) Use a graph of f '' to estimate the xcoordinates of the inflection points (Round your Question Consider the function below f(x) = x1/x, x >Show that F(X) = (X − 1) Ex 1 is an Increasing Function for All X > 0 ?



Activation Functions Fundamentals Of Deep Learning




Second Derivative Calculus Tutorials
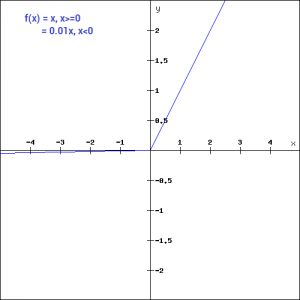
For all x and y such that −1 < x < 1 (otherwise the denominator f X (x) vanishes) and < < (otherwise the conditional probability degenerates to 0 or 1) One may also treat the conditional probability as a random variable, — a function of the random variable X , namely, If f R → R is a twice differentiable function such that f '' (x) > 0 for all x ∈ R, and f f(1/2) = 1/2, Sarthaks eConnect Largest Online Education Community If f R → R is a twice differentiable function such that f '' (x) > 0 for all x ∈ R, and f f(1/2) = 1/2, f(1) = 1, then Login Remember Register f (x) = x = {x if x ≥ 0 −x if x < 0 So, lim x→0 x = lim x→0 x = 0 and lim x→0− x = lim x→0− ( − x) = 0 Therefore, lim x→0 x = 0 which is, of course equal to f (0) To show that f (x) = x is not differentiable, show that f '(0) = lim h→0 f (0 h) − f (0



Gradients Stationary Points




Limits



Differentiable Function Wikipedia
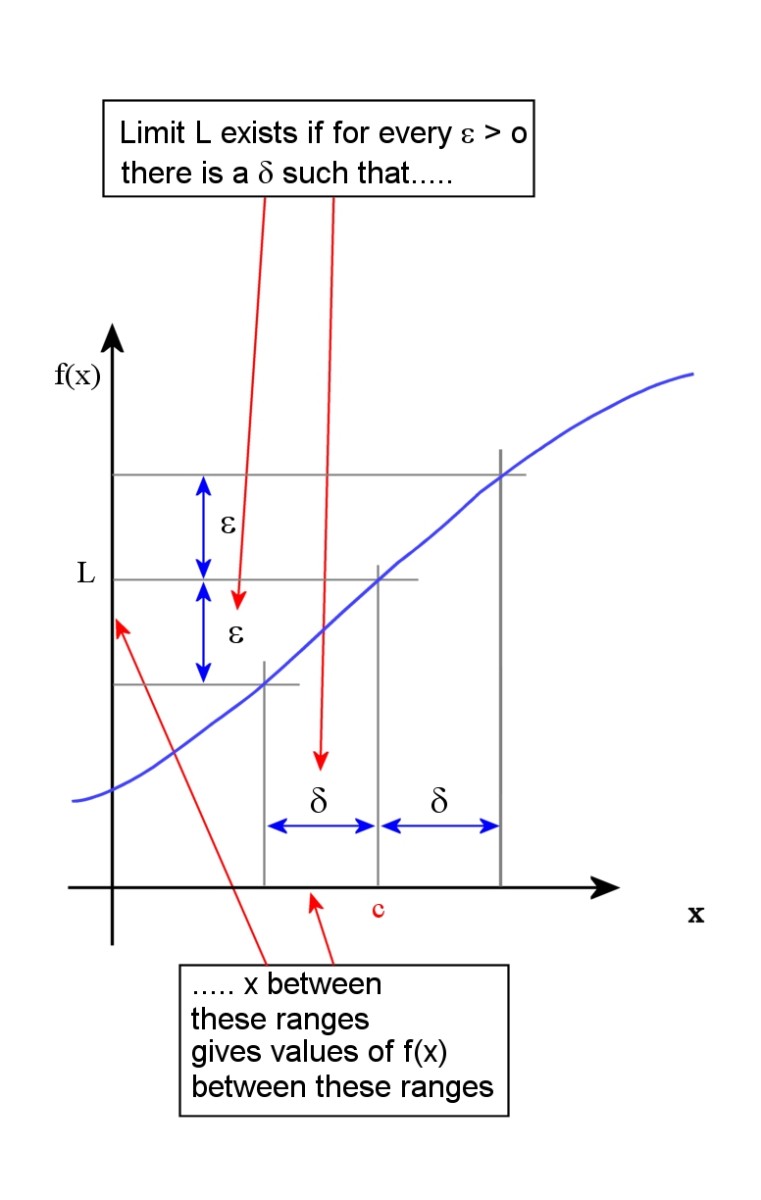



What Is Calculus A Beginner S Guide To Limits And Differentiation Owlcation




4 3 Connecting F And F With The Graph Of F Magic Light Calculus




Let F R R Be A Function Such That F X X 2 For All Xepsilon R Then At X 0 F Is



2 4 Differentiability Vs Continuity



Gradients Stationary Points



Http Users Math Msu Edu Users Gnagy Teaching 10 Fall Mth234 W6 234 H Pdf
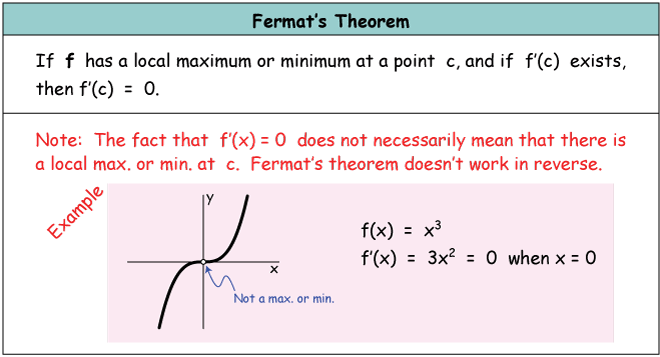



Reading Curve Sketching Business Calculus



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations



What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora




Section 3 4 Concavity And The Second Derivative Test Ppt Video Online Download



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf



Www Beachwoodschools Org Downloads Ab 3 42 Pdf



What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora




Increasing Decreasing Functions Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes



Sage Calculus Tutorial Differentiability




A Function F R R Satisfies The Equation F X Y F X F Y For All Xy E R F X 0 Suppose That The Function Is Differentiable At X 0 And F 0 2 Prove That F X Mathematics Topperlearning Com A5z3qnjj




How To Find The Equation Of A Tangent Line 8 Steps




Find Limits Of Composition In The Graph Of F Mathematics Stack Exchange



Http Www Math Ust Hk Majhu Math3 Rudin Homework18 Pdf



Minimizing The Cost Function Gradient Descent By Xuankhanh Nguyen Towards Data Science




4 3 How Derivatives Affect The Shape Of A Graph Mathematics Libretexts
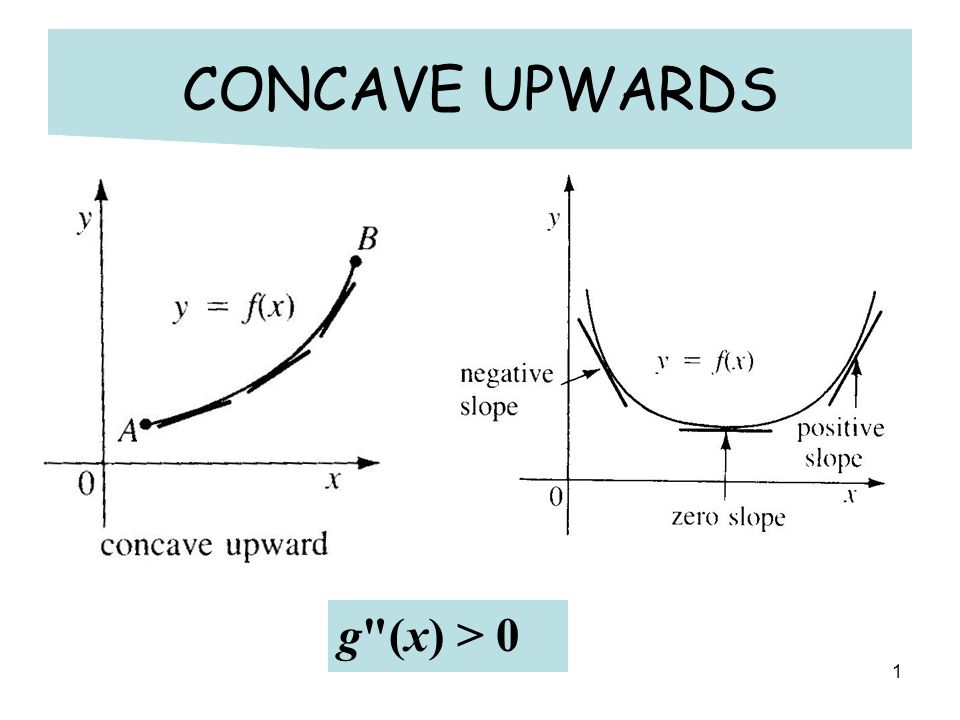



1 Concave Upwards G X 0 2 Concave Downwards G X 0 Negative Slope Y G X Positive Slope Zero Slope Ppt Download



F X 0




Let F X Is A Function Continuous For All X In Rexcept At X 0 Such That F X 0 X In Oo 0 And F X 0 X In 0 Oo If Lim X 0 F X 3




Edexcel Core Mathematics C1 May 17



Www Southhadleyschools Org Cms Lib Ma Centricity Domain 11 Theorems Pdf



Increasing And Decreasing Functions




4 2 The Mean Value Theorem Mathematics Libretexts
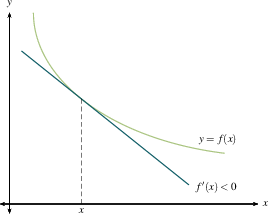



F Vs F



Critical Points




Derivative And Tangent Line




How To Find The Equation Of A Tangent Line 8 Steps




4 1 Extreme Values Of Functions Mathematics Libretexts



Find Real Values For Fx 0 Youtube




Curve Sketching




Let F Be Continuous On A B And Differentiable On A B If F X Is Strictly Increasing On A B Then F X 0 For All X In A B And If



Http Maths Dur Ac Uk Dma0wjz B1 Anlec1 Pdf




Is My Solution Correct To Prove That F X 0 For All X In A B Mathematics Stack Exchange



Www Crsd Org Cms Lib5 Pa Centricity Domain 787 3 1 3 4 ap practice mc Key Pdf




Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com



Do Local Extrema Occur If And Only If F X 0 Brilliant Math Science Wiki




Check Whether F X Is Greater Than Zero Or Not For All X In b R Mathematics Stack Exchange




There Exists A Function F Such That Fx 0 F X 0 And Gauthmath




The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below What Are All Of The Real Solutions Of F X 0 Brainly Com




Question Video Finding The Solution Set Of A Quadratic Equation Graphically Nagwa



Solution Use The Graph Of The Function To Estimate A F 2 B F 4 C All X Such That F X 0 I Can 39 T Show The Graph On Here It Won 39 T Copy And




Ex 5 1 18 For What Value Of Is F X Continuous At X 0 1




Use The Graph Of F To Determine Where A F X 0 And Chegg Com




Match The Conditions F X Less Than 0 And F X Less Than 0 With One Of The Graphs In The Figure Study Com



Find The Values Of X For Which F X 0 Youtube



Inflection Points




Cc The Second Derivative




Turning Points And Nature Iitutor



Www Ebnet Org Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 816 17 18 chapter 5 period 3 answer key Pdf



What Is The Maclaurin Series X 0 For F X Sin 2x Socratic




Curve Sketching F X



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity



7 4 Logarithmic Differentiation



Let ƒ 0 2 R Be A Twice Differentiable Function Such That ƒ X 0 For All X 0 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
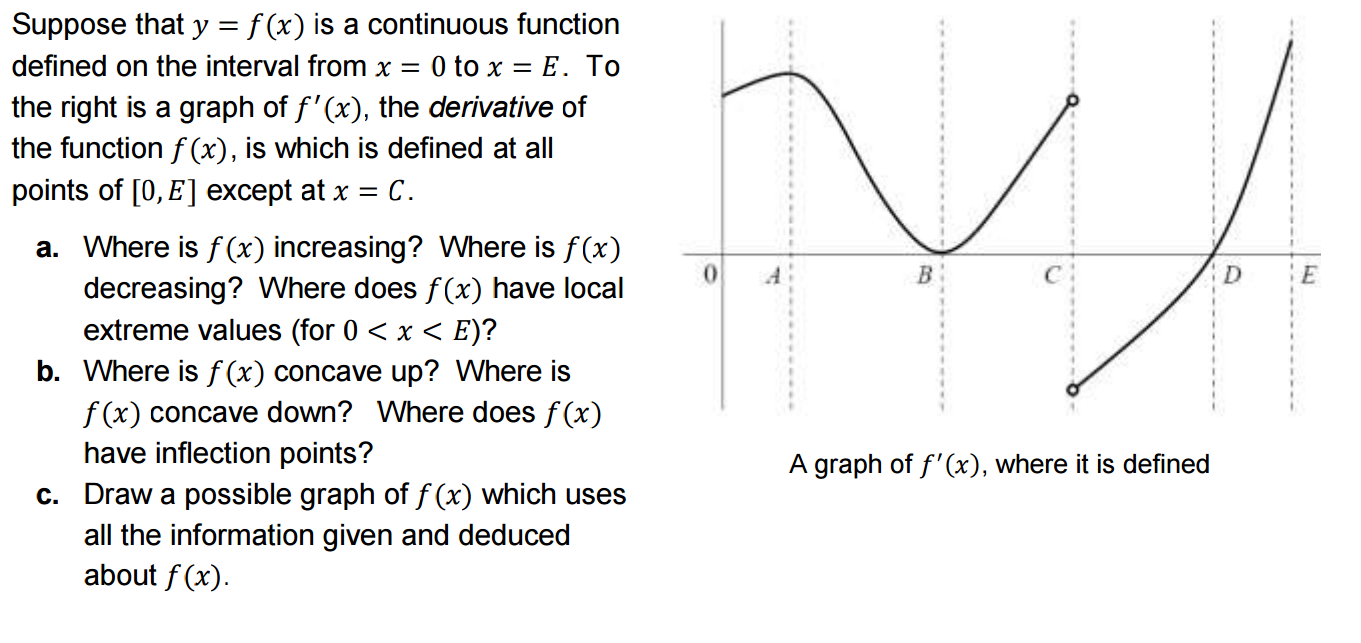



Suppose That Y F X Is A Continuous Function Defined Chegg Com




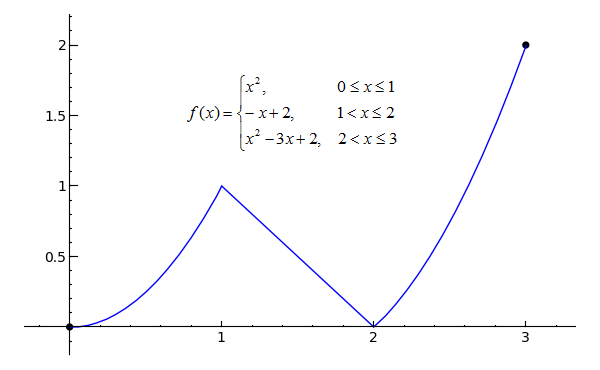
Piecewise Function From Wolfram Mathworld




Misc 16 Let F Be A Function Defined On A B F X 0




Finding Decreasing Interval Given The Function Video Khan Academy
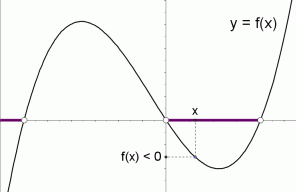



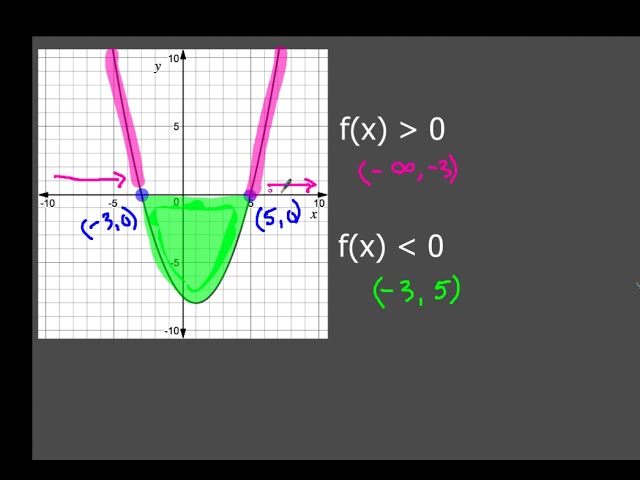
Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0




At What Values Of X Does F X 0 Brainly Com
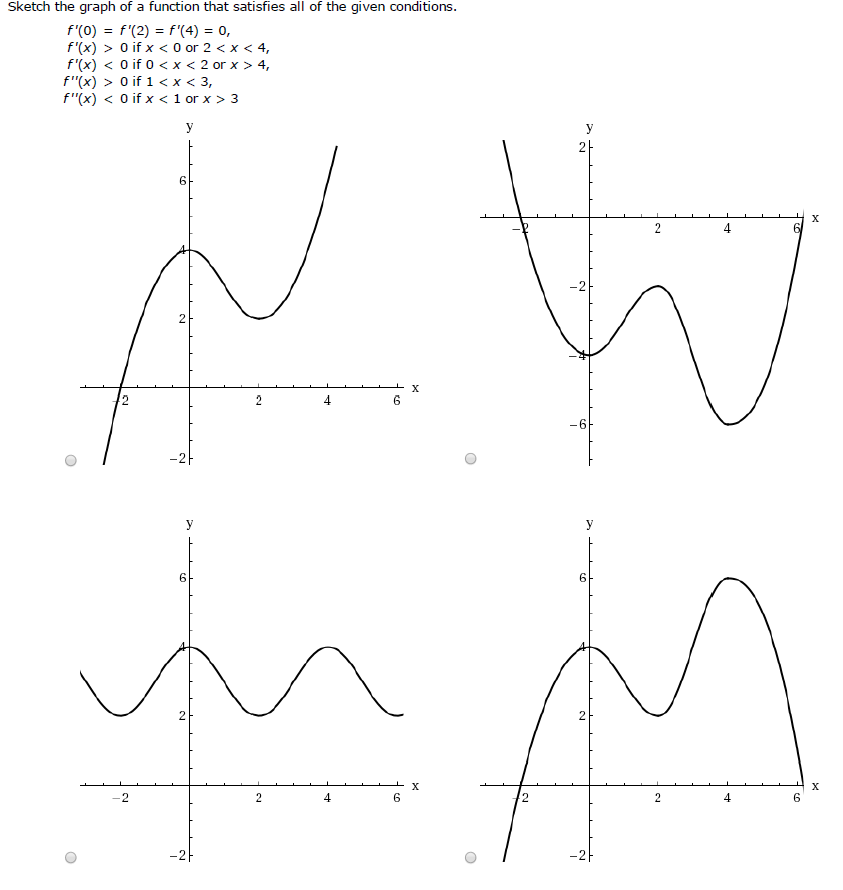



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com



Theorem For Limits Of Composite Functions Video Khan Academy



Calculus Revision Maths First Institute Of Fundamental Sciences Massey University



Critical Points




Activation Functions Fundamentals Of Deep Learning



Web Viu Ca Pughg Summer12 Math121m12n01 Secondderivativenotes Pdf



No comments:
Post a Comment